Key Takeaways
-
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) combines technology, policies, processes and people to protect sensitive data from unauthorized access or transfer.
-
Modern DLP solutions use encryption, real-time monitoring and advanced analytics to detect and prevent data breaches.
-
Common threats include malware, phishing, device loss/theft and human error—all of which can lead to data exposure.
-
Key DLP features include data leakage protection, policy enforcement, cloud integration, incident response and real-time alerts.
-
Best practices for DLP: Define clear policies, identify sensitive data, apply role-based access, monitor and encrypt data, automate incident response and educate employees.
-
Types of DLP solutions: Network DLP (data in motion), Endpoint DLP (device-level protection), and Storage DLP (data at rest).
-
Implementing DLP reduces risk, ensures compliance and strengthens your organization’s first line of defense against cyber threats.
What Is Data Loss Prevention (DLP)?
Data Loss Prevention or DLP is a strategic combination of technology, processes, policies and people to identify, monitor and prevent unsafe or unauthorized sharing or transfer of sensitive data. A robust data loss prevention solution helps safeguards corporate information while ensuring compliance with regulatory standards. Modern DLP tools leverage advanced analytics, encryption, and real-time monitoring to detect suspicious activity and enforce security protocols.
Why Companies Should Implement Data Loss Prevention Software
By implementing data loss prevention software, organizations can reduce overall risk exposure, protect endpoints—such as mobile devices, printers and servers—and respond to ongoing cyber threats.
Common Data Security Threats DLP Software Helps Prevent
Malware
Malware is malicious software designed to disrupt, damage, or gain access to your systems to steal, encrypt or destroy data.
Phishing
Phishing is a type of cyber attack that uses deceptive emails or messages to trick users into revealing sensitive information or downloading harmful attachments. It often uses urgency and emotional language to get users to perform certain actions, such as clicking links, entering information, downloading attachments, and more.
Loss or Theft
Without proper encryption or remote wiping capabilities, physical devices that are stolen or lost can lead to data breaches or exposure. Hardware often contains sensitive information of both the organization and the individual, which becomes vulnerable to exploitation once a device is lost.
Human Error
According to IBM’s 2025 Cost of a Data Breach Report, the global average cost of a data breach is 4.4 million dollars (USD)—and sometimes the most seemingly innocuous decision or mistake can lead to these costly outcomes. Human error can often coincide with one of the aforementioned data threats. Whether clicking a malicious link that compromises data or approving a Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) push notification that grants a criminal access to your corporate network, it’s vital that employees are adequately trained in cyber security best practices.
Key Features of Data Loss Prevention Solutions
Encryption
-
By encrypting your data, you ensure that only authorized users have access to it while it’s in transit or at rest.
Incident Response & Reporting
-
Through centralized dashboard, incidents can be collected, viewed and managed for quick troubleshooting, analysis and auditing.
Alerts
-
Alerts are real-time notifications that are triggered to prevent harmful actions from taking place. It not only helps prevent compromisable situations but also educates users about data leakage protection.
Cloud Integration
-
Through the use of cloud integration, you can enforce policies across all endpoints, apps, and data repositories from a single console.
Policy Enforcement
-
By enforcing policies, rules are applied to how data is handled, such as blocking, encrypting, or quarantining. Policies help ensure compliance with certain regulations or regulatory bodies.
Real-Time Monitoring
-
With the right solutions, organizations can track data across networks, email and applications, monitoring sensitive data that leaves and comes into the organization.
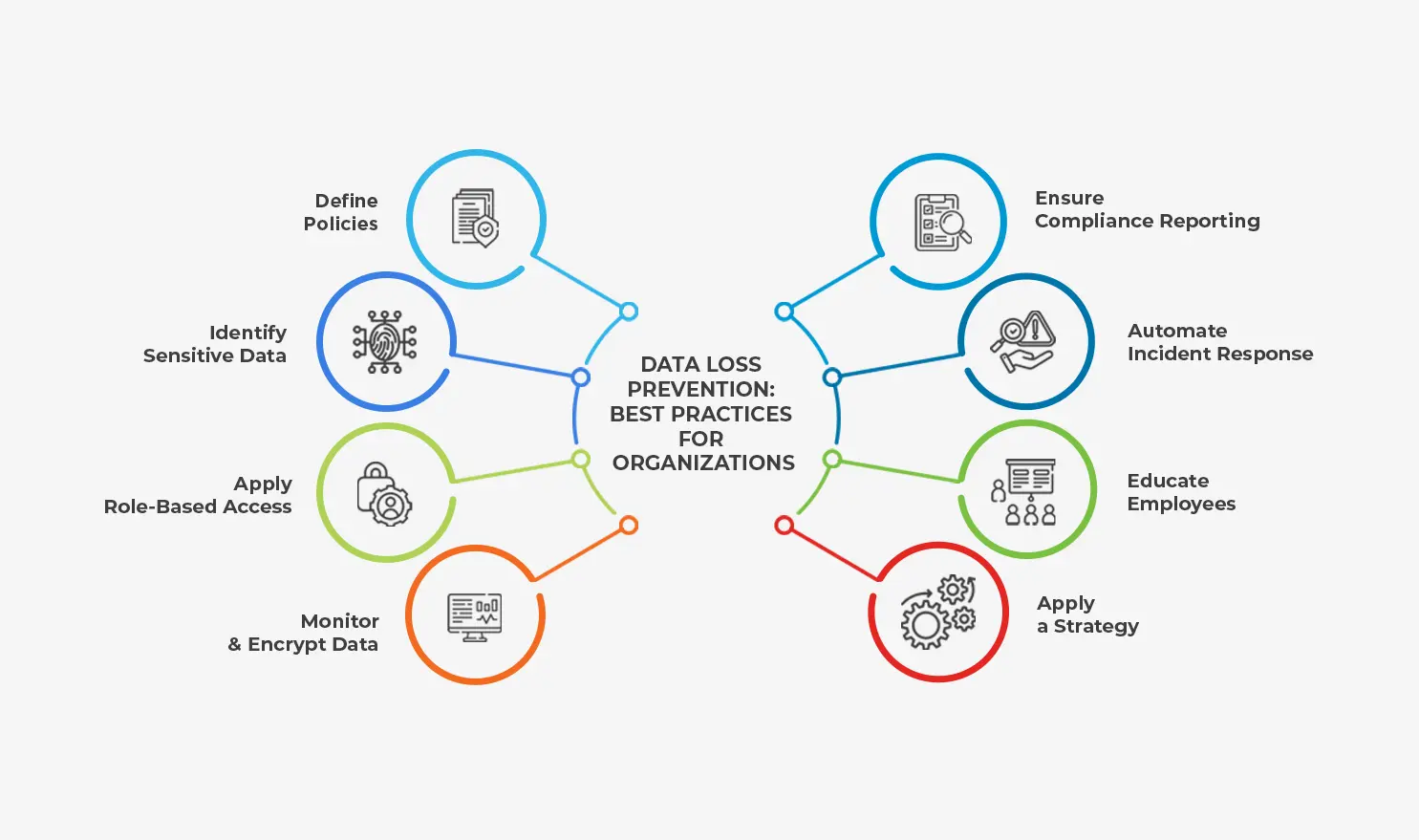
Data Loss Prevention Best Practices for Organizations
-
Define clear policies – Ensure that policies are aligned with and meet regulatory compliance.
-
Identify sensitive data – Map where sensitive data resides and what classifies as sensitive data.
-
Apply role-based access – Grant access to data according to user role and responsibility, ensuring that authorization is restricted accordingly.
-
Monitor and encrypt data – Ensure real-time visibility on data moving in transit and at rest.
-
Ensure compliance reporting – Generate audits and reports for stakeholders on the status of compliance, incidents, response time, policy changes and more.
-
Automate incident response – Create workflow processes to notify admins or isolate devices automatically, speeding up remediation and mitigating damage.
-
Educate employees – Train staff on best practices for handling data and why data loss protection matters. Use alerts to notify users when policies are violated.
-
Apply a strategy – Have a strategy in place for both incident response and disaster recovery. Preparedness helps ensure that damage is mitigated.
Types of DLP Solutions to Protect Sensitive Data
Network DLP
Network DLP primarily monitors and protects data in motion across corporate networks—web, email and certain apps. It focuses on detecting and preventing unauthorized data transfers, such as confidential sharing or improper uploading.
Endpoint DLP
Endpoint DLP extends protection to physical devices, such as mobile devices, computers, printers, and other endpoints. By deploying agents to the device, this solution monitors applications and processes. It also controls and protects against sensitive data being copied to removable hardware such as USB drives.
Storage DLP
Storage DLP focuses on data at rest by scanning databases, file servers, or cloud repositories for sensitive information. It applies encryption, access controls and policies to ensure that stored data remains secure.
Conclusion
In today’s evolving cyber threat landscape, data loss prevention solutions are no longer optional—they’re business-critical. Implementing the best data loss prevention software and combining DLP tools, strong encryption, real-time monitoring and thorough employee training ensures your organization can:
-
Detect, prevent and respond to data breaches before they escalate.
-
Stay compliant, reduce risk and maintain trust.
-
Prioritize scalability, cloud integration and advanced analytics.
When it comes to sensitive data, prevention is your first line of defense against cyber threats. Explore how SOTI MobiControl XS (SOTI MobiControl & SOTI XSight) delivers advanced data loss prevention capabilities—combining real-time monitoring, policy enforcement and endpoint security—to keep your sensitive data safe.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is the difference between DLP and endpoint security?
A: DLP or Data Loss Prevention is the strategic combination of technology, processes, policies and people to identify, monitor and prevent unsafe or unauthorized sharing or transfer of sensitive data. Endpoint security specifically focuses on the protection of devices (endpoints), such as mobile devices, printers, rugged devices, scanners, and more, from cyber security threats.
Q: Which types of sensitive data should be protected first?
A: Data should be categorized and protected based on what is considered sensitive, business-critical and regulated. After that, priority can be expanded to less sensitive data.
Q: How to prevent data breaches?
A: There’s no single way to prevent data breaches, but organizations can reduce risk by implementing strong access controls, encrypting sensitive data, using real-time monitoring to detect suspicious activity, reinforcing employee training and automating incident response for maximum protection.
Q: What types of data does DLP protect?
A: DLP protects against personally identifiable information, financial records, customer and employee data, compliance-related information, broad corporate data and more.